Efficient removal of residual oxygen from inert gases
A highly efficient process for the removal of residual oxygen from inert gases is suggested, which bypasses the use of highly reactive substances and avoids contamination of inert gases.
Challenge
Most materials form oxide layers on their surface at room temperature and in air. This is often not desirable and can be disruptive in oxygen sensitive processes. In order to reduce or avoid material oxidation, oxygen sensitive processes are often conducted in ultra high vacuum (UHV) conditions. UHV facilities can be expensive in purchase and operation, while materials with low vapor pressure cannot be processed at such conditions. An alternative is the usage of an oxygen-free atmosphere, namely inert gas (e.g. argon and nitrogen) atmosphere. However, even 99.999% clean inert gases (purity 5.0) still contain residual oxygen, which can be significantly disruptive. In UHV facilities often titanium swarfs are used as oxygen traps, which induce the formation of TiO2 and, hence, reduction of the oxygen partial pressure. SiH4 can be used as oxygen trap as well, which reacts with oxygen in the inert gas under formation of SiO2 and H2. However, SiH4 is a highly reactive substance, while H2 is a highly reactive reaction product, which (after removal of oxygen) remains as contaminant in the inert gas.
Our Solution
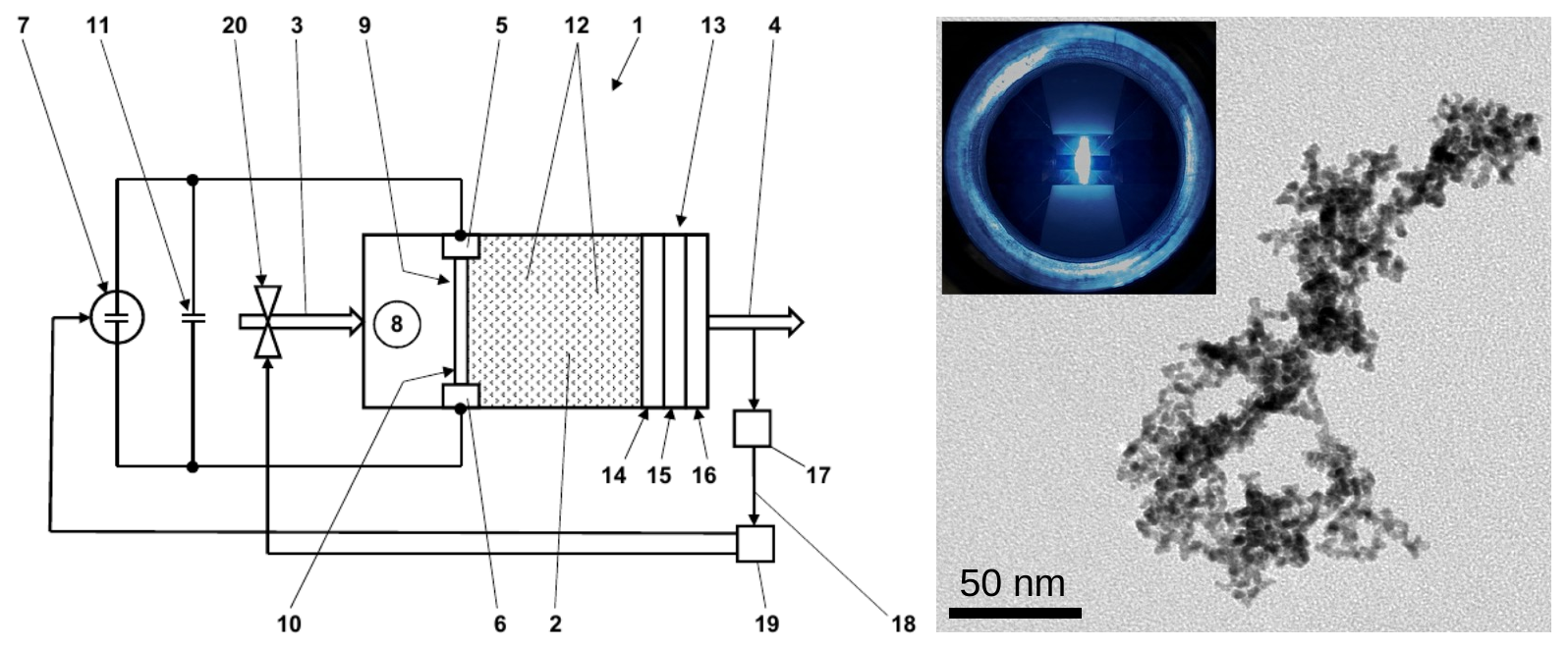
Scientists from the Clausthal University of Technology have developed a procedure, which bypasses the aforementioned challenges and removes the residual oxygen from inert gases. Thereby, a voltage is applied between two electrodes, which are adjoined to the nobel gas, followed by electric or gas discharge in the nobel gas. This induces the removal or erosion of metal from at least one of the electrodes, which leads to formation of nanoparticles in the inert gas. The latter and the general tendency of metallic nanoparticles (e.g. iron and aluminum) to oxidation are well known. However, the present invention impressively exploits the formation of metallic nanoparticles by spark synthesis and enables the reduction of the residual oxygen in an inert gases (e.g. argon and nitrogen) to extremely low contents of 1 x 10-13 ppm and even beneath. According to the invention, double passage of the process allows to reach a residual oxygen content of 3.5 x 10-15 ppm. The metallic nanoparticles, which are formed by spark synthesis and intercept the oxygen, are themselves separated by HEPA filters (or similar). Thus, the residual oxygen from the treated inert gas is bound in form of metal oxides and separated in filters.
Fig. 1: Device for removal of residual oxygen from inert gases (left side) and exemplary TEM image showing metallic nanoparticles (right side) synthesized with the spark generator (inset in the TEM image). Source: German patent application DE102021121928A1, international patent application WO2023025716A1 and Mr. V. Olszok (TU Clausthal).
Advantages
- Highly efficient removal of residual oxygen from inert gases
- No highly reactive substances involved
- Easy implementation in existing or established production and processing lines
- Manageable efforts and costs
Applications
- Metal processing
- Semiconductor production
- Additive manufacturing
- 3D printing
- Chemical industry
- Packaging industry
- Welding
- Reflow soldering
- Laser cutting
Development Status
The process has been successfully developed and experimentally approved on laboratory scale. Prototype available. System and process upscaling aimed.
Patent Status
German patent application: DE102021121928A1
International patent application: WO2023025716A1
Patent holder: Clausthal University of Technology
Contact
Dr. Mirza Mackovic
Patent Manager Technology
E-Mail: This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.
Tel.: +49 551 30724 153
Reference: MM-2336-T282