
Mechanical propeller emergency stop mechanism
A novel technology for the mechanical stop of one or multiple rotating propellers is suggested. The emergency propeller stop is achieved by combining a material-mediated engagement mechanism with temporal coordination of rotor contact.
Challenge
Safety systems based on GPS, optical and acoustic sensors are widely spread in the manned and unmanned aerospace technology and engineering. The processing of information stemming from these sensors can be implemented with a flight controller, which can for instance be found in vertical take-off and landing (VTOL) aircraft. VTOL aircraft are often equipped with multiple rotors, which can be aligned and operated in vertical and horizontal configuration on demand. Electronic emergency rotor stop systems, which are used for a prompt stop of a rotor before contact with an object occurs, are available. However, complex electronics are often prone to errors and failure, which can have a negative impact on reliability and overall system safety.
Our solution
Scientists from the University of Hannover have developed a purely mechanical system and mechanism, which enables a rotor stop within few milliseconds as soon as a first rotor contact with an object occurs. For a single rotor setup (see Fig. 1) a rebound strap is fixed in the outer region of the rotor, in order to allow free rotor movement. In its fixed position, the rebound strap is under tension. As soon as the strap is released, the strap moves towards the rotating propeller due to material relaxation. The strap entangles in the rotor and stops its rotation immediately. A more advanced emergency stop system is achieved for a two-rotor configuration by using material-specific, circular cage structures, which surround the rotors (see Fig. 2). The cage structures exhibit channels for free rotor movement. Black ropes are attached to the cage and connected via red ropes with each other. When the cage touches or gets touched by an object, the cage material deforms. This triggers a mechanism, which pushes the black ropes towards the moving rotors, followed by rotation stop. The entanglement of a rope in one rotor triggers a second mechanism via the red ropes, which pull the black ropes towards the second rotor and stop its movement. The sensitivity of cage deformation and propeller stop mechanism is controllable by used material.
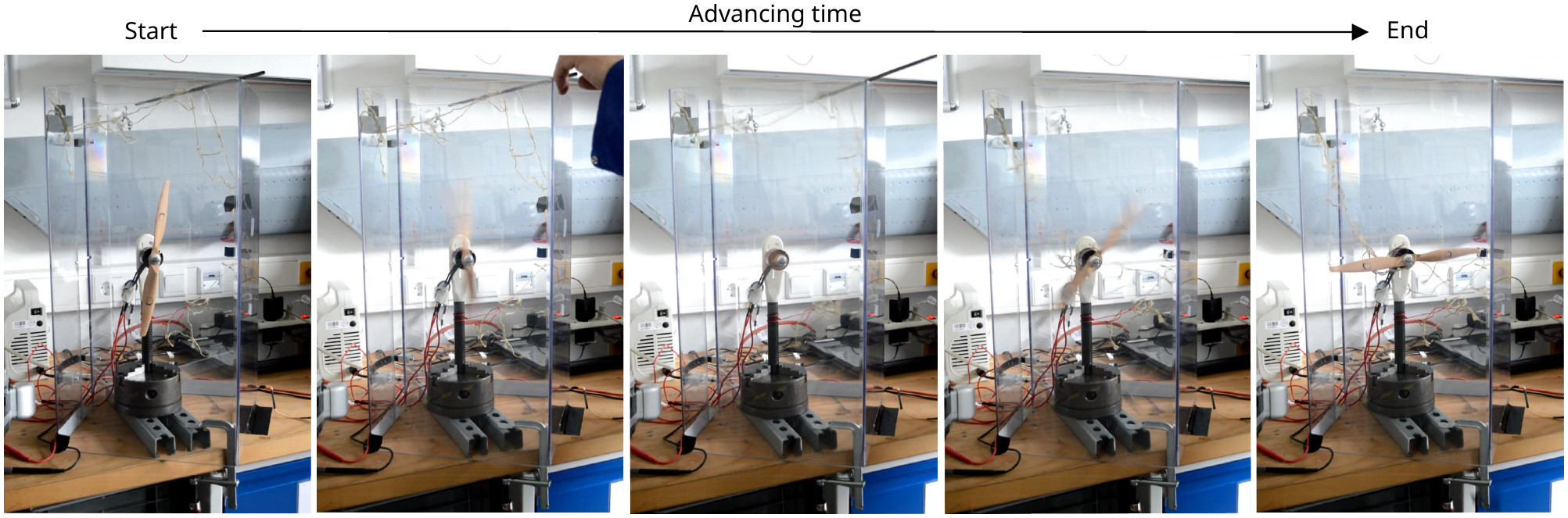 Fig. 1: Experimental setup showing the emergency mechanism for the stop of one propeller with a rebound strap (source: Prof. Sindelar and Mr. Bauer, University of Hannover - University of Applied Sciences and Arts).
Fig. 1: Experimental setup showing the emergency mechanism for the stop of one propeller with a rebound strap (source: Prof. Sindelar and Mr. Bauer, University of Hannover - University of Applied Sciences and Arts).
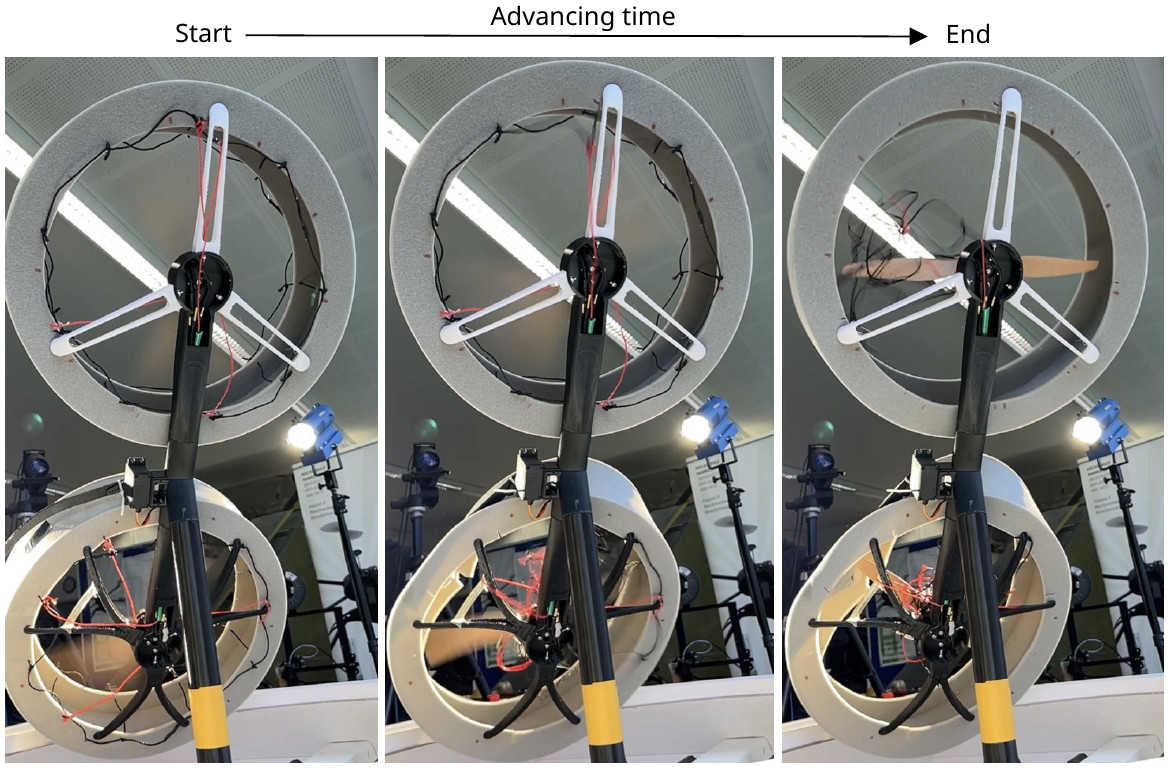 Fig. 2: Prototype of the mechanical propeller emergency stop mechanism for a twin rotor configuration (source: Prof. Sindelar and Mr. Bauer, University of Hannover - University of Applied Sciences and Arts).
Fig. 2: Prototype of the mechanical propeller emergency stop mechanism for a twin rotor configuration (source: Prof. Sindelar and Mr. Bauer, University of Hannover - University of Applied Sciences and Arts).
Advantages
- Safe and reliable propeller stop with a fast reaction time
- Cost-efficient and purely mechanical propeller stop system
- No electronics involved
Applications
- Manned and unmanned aerospace technology and engineering
- VTOL aircraft
Development Status
Technology successfully developed. System functionality experimentally approved. Prototype available.
Patent Situation
German patent application filed: DE102022134204.2
Patent applicant: University of Hannover - University of Applied Sciences and Arts
Contact
Dr. Mirza Mackovic
Patent Manager Technology
E-Mail: Diese E-Mail-Adresse ist vor Spambots geschützt! Zur Anzeige muss JavaScript eingeschaltet sein!
Phone: +49 551 30724 153
Reference: CPA-2404-HsH
